| Lesson 3 | Arrays |
| Objective | Describe how arrays are declared and initialized. |
Declare and initialize Arrays in Java
When an array is declared, the array's dimensions must be specified using a pair of matching braces (i.e.,
To add to this confusion, multidimensional arrays may be specified with brace sets to the left or right of the array identifier.
[]). Java provides a lot of lexibility on how these braces may be placed. They may be placed to the right of the array type or to the right of the array identifier. Zero or more spaces may be placed around each brace. Each of the following array declarations are equivalent:
int[]i; int[] i; int []i; int i[]; int [ ] i; int i [ ];
To add to this confusion, multidimensional arrays may be specified with brace sets to the left or right of the array identifier.
int[] j[]; int []j[]; int[][] j; int j[][];
Java Array Dimensions
Technically, Java does not have multidimensional arrays. Multidimensional arrays are arrays of arrays. In practice, this technicality doesn't mean much. However, you should note that it is possible to have an array of arrays in which the array elements are of different sizes. The following array declaration illustrates this point. It declares
oddArray as an array of different size arrays.
int[][] oddArray = {{1},{2,3},{4,5,6}};
- What is an array?
An array is an object that stores a collection of values. The fact that an array itself is an object is often overlooked. I will reiterate, "an array is an object itself", which implies that it stores references to the data it stores. Arrays can store two types of data:
- A collection of primitive data types
- A collection of objects
An array of primitives stores a collection of values that constitute the primitive values themselves. (With primitives, there are no objects to reference.) An array of objects stores a collection of values, which are in fact heap-memory addresses or pointers. The addresses point to (reference) the object instances that your array is said to store, which means that object arrays store references (to objects) and primitive arrays store primitive values. The members of an array are defined in contiguous (continuous) memory locations and hence offer improved access speed. (You should be able to quickly access all the students of a class if they all can be found next to each other.)
Note: Arrays are objects and refer to a collection of primitive data types or other objects.
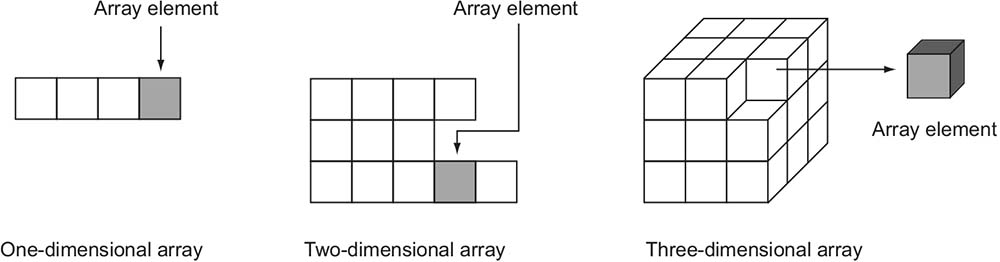
In Java, you can define one-dimensional and multidimensional arrays. A one-dimensional array is an object that refers to a collection of scalar values. A two-dimensional (or more) array is referred to as a multidimensional array. A two-dimensional array refers to a collection of objects in which each of the objects is a one-dimensional array. Similarly, a three-dimensional array refers to a collection of two-dimensional arrays, and so on. Figure 4-3 depicts a one-dimensional array and multidimensional arrays (twodimensional and three-dimensional). Note that multidimensional arrays may or may not contain the same number of elements in each row or column, as shown in the two-dimensional array in figure 4-3. Creating an array involves three steps, as follows:
In Java, you can define one-dimensional and multidimensional arrays. A one-dimensional array is an object that refers to a collection of scalar values. A two-dimensional (or more) array is referred to as a multidimensional array. A two-dimensional array refers to a collection of objects in which each of the objects is a one-dimensional array. Similarly, a three-dimensional array refers to a collection of two-dimensional arrays, and so on. Figure 4-3 depicts a one-dimensional array and multidimensional arrays (twodimensional and three-dimensional). Note that multidimensional arrays may or may not contain the same number of elements in each row or column, as shown in the two-dimensional array in figure 4-3. Creating an array involves three steps, as follows:
- Declaring the array
- Allocating the array
- Initializing the array elements
Multidimensional Arrays in Java
The following array arr[i][j][k] is simply an array, of arrays, of arrays.
If you know how arrays work, you know how multidimensional arrays work.
or, with initialization:
If you know how arrays work, you know how multidimensional arrays work.
int[][][] threeDimArr = new int[4][5][6];
or, with initialization:
int[][][] threeDimArr = { { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 } }, { { 5, 6 }, { 7, 8 } } };
Once an array is declared, it must be created. This can be done using an array initializer or using the
The above declares, creates, and initializes an array of five int values. Arrays of arrays may be specified by nesting array initializers.
Array initializers work well for small arrays but are impractical for arrays that contain more than a few elements. To create larger arrays, use the
The above statement declares and initializes an array of 100
The above notation is also equivalent to the following:
One array can be copied to another array by using the method
new operator followed by an array dimension expression. Array initializers are used as follows:
int[] i = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
The above declares, creates, and initializes an array of five int values. Arrays of arrays may be specified by nesting array initializers.
int[][] i = {{1,2,3}, {4,5,6}, {7,8,9}};
Array initializers work well for small arrays but are impractical for arrays that contain more than a few elements. To create larger arrays, use the
new operator followed by the array type and the array size within braces.
String[] s = new String[100];
The above statement declares and initializes an array of 100
String objects. You can also specify multidimensional arrays using this notation:
String[][] s = new String[200][50];
The above notation is also equivalent to the following:
String[][] s = new String[200][]; for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) s[i] = new String[50];
One array can be copied to another array by using the method
static void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length)
This page discusses the components of ArrayCopy in Java
The arraycopy method basically copies an array from the specified source array, beginning at the specified position, to the specified position of the destination array. The last parameter is the number of elements that you want to copy.
There are questions in the exam on System.arraycopy. Review the
JavaDoc description for the arraycopy method:
JavaDoc description for the arraycopy method:
public static void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length)
- Copies an array from the specified source array, beginning at the specified position, to the specified position of the destination array.
- A subsequence of array components is copied from the source array referenced by src to the destination array referenced by dest.
- The number of components copied is equal to the length argument.
- The components at positions srcPos through srcPos+length-1 in the source array are copied into positions destPos through destPos+length-1, respectively, of the destination array.
- If the src and dest arguments refer to the same array object, then the copying is performed as if the components at positions srcPos through srcPos+length-1 were first copied to a temporary array with length components and then the contents of the temporary array were copied into positions destPos through destPos+length-1 of the destination array.
- If dest is null, then a NullPointerException is thrown.
- If src is null, then a NullPointerException is thrown and the destination array is not modified.
Java Language Reference
Otherwise, if any of the following is true, an ArrayStoreException is thrown and the destination is not modified:
- The src argument refers to an object that is not an array.
- The dest argument refers to an object that is not an array.
- The src argument and dest argument refer to arrays whose component types are different primitive types.
- The src argument refers to an array with a primitive component type and the dest argument refers to an array with a reference component type.
- The src argument refers to an array with a reference component type and the dest argument refers to an array with a primitive component type.
Otherwise, if any of the following is true, an IndexOutOfBoundsException is thrown and the destination is not modified:
- The srcPos argument is negative.
- The destPos argument is negative.
- The length argument is negative.
- srcPos+length is greater than src.length, the length of the source array.
- destPos+length is greater than dest.length, the length of the destination array.
Otherwise, if any actual component of the source array from position srcPos through srcPos+length-1 cannot be converted to the component type of the destination array by assignment conversion, an ArrayStoreException is thrown.
In this case, let k be the smallest nonnegative integer less than length such that src[srcPos+k] cannot be converted to the component type of the destination array; when the exception is thrown, source array components from positions srcPos through srcPos+k-1 will already have been copied to destination array positions destPos through destPos+k-1 and no other positions of the destination array will have been modified.
(Because of the restrictions already itemized, this paragraph effectively applies only to the situation where both arrays have component types that are reference types.)
In this case, let k be the smallest nonnegative integer less than length such that src[srcPos+k] cannot be converted to the component type of the destination array; when the exception is thrown, source array components from positions srcPos through srcPos+k-1 will already have been copied to destination array positions destPos through destPos+k-1 and no other positions of the destination array will have been modified.
(Because of the restrictions already itemized, this paragraph effectively applies only to the situation where both arrays have component types that are reference types.)
- Parameters: src - the source array. srcPos - starting position in the source array.
- dest - the destination array. destPos - starting position in the destination data. length - the number of array elements to be copied.
- Throws: IndexOutOfBoundsException - if copying would cause access of data outside array bounds.
- ArrayStoreException - if an element in the src array could not be stored into the dest array because of a type mismatch.
- NullPointerException - if either src or dest is null.
When an array is created, its elements are automatically initialized as described in the Module "Java Language Fundamentals."
Java Array Declarations - Quiz
Click the Quiz link to check your understanding of variable declarations.
Java Array Declarations - Quiz
Java Array Declarations - Quiz