EntityManager.find() method.
This method takes the entity class and its primary key and returns the managed entity instance or null if no match is found.
| Lesson 5 | Finding by Primary Key |
| Objective | Use the primary key to retrieve a persistent entity with JPA. |
EntityManager.find() method.
This method takes the entity class and its primary key and returns the managed entity instance or null if no match is found.
In Java EE 8, the JPA API resides in the javax.persistence package. Here’s how you can find a Customer entity by its primary key:
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.PersistenceContext;
@Stateless
public class CustomerService {
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager em;
public Customer findCustomerById(Long id) {
return em.find(Customer.class, id);
}
}
Jakarta EE 10 moved JPA to the jakarta.persistence package. The functionality is the same, but the imports change:
import jakarta.persistence.EntityManager;
import jakarta.persistence.PersistenceContext;
import jakarta.ejb.Stateless;
@Stateless
public class CustomerService {
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager em;
public Customer findCustomerById(Long id) {
return em.find(Customer.class, id);
}
}
The following two diagrams illustrate how entity retrieval evolved in Java:
findByPrimaryKey() EJB call chain used in J2EE applications.EntityManager.find() flow used in Java EE 8 and Jakarta EE 10.findByPrimaryKey() Call Chain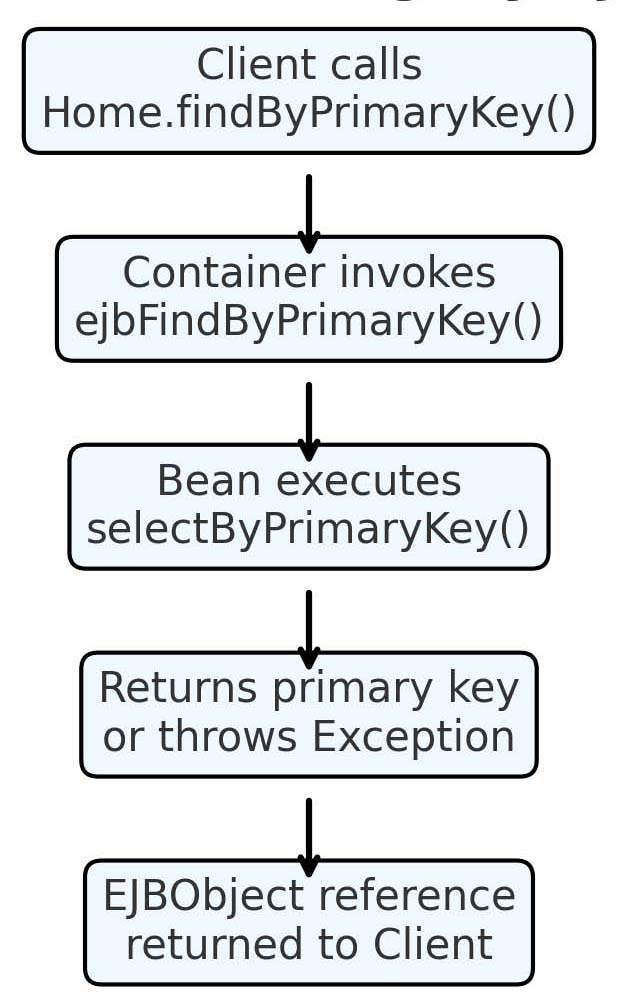
EJBObject or throwing a finder‑related exception.
EntityManager.find() Flow (Java EE 8 / Jakarta EE 10)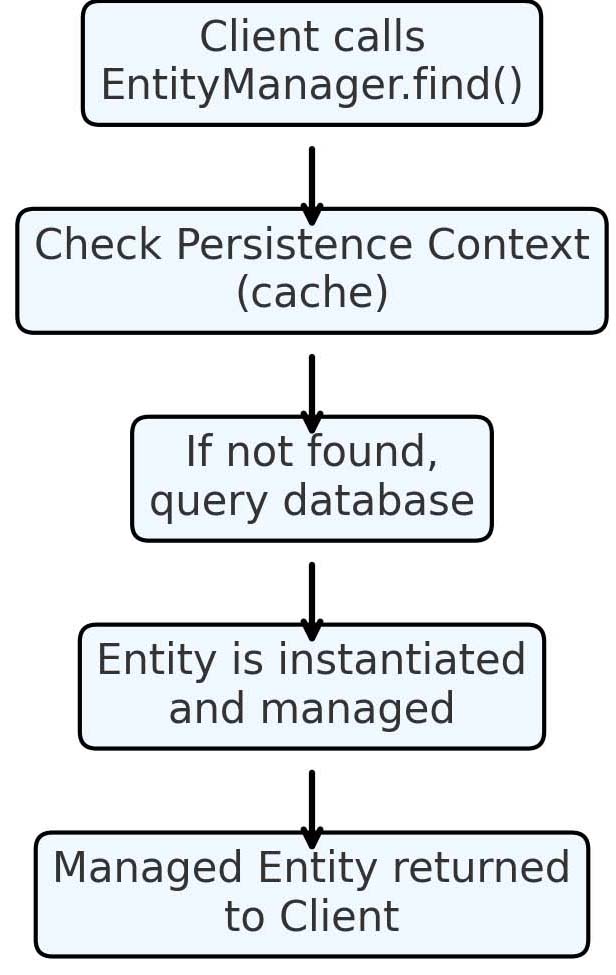
EntityManager.find(), which checks the persistence context first and
queries the database if necessary, returning a managed entity instance or null.
null.FinderException — just check for null.
Customer customer = customerService.findCustomerById(1001L);
if (customer != null) {
System.out.println("Found: " + customer.getName());
} else {
System.out.println("Customer not found.");
}
In addition to find(), JPA provides query mechanisms such as JPQL and the Criteria API to locate entities by non-primary key attributes. These will be covered in later modules.
Click the quiz link below to test your understanding of using JPA to find entities.
Finding Entities - Quiz