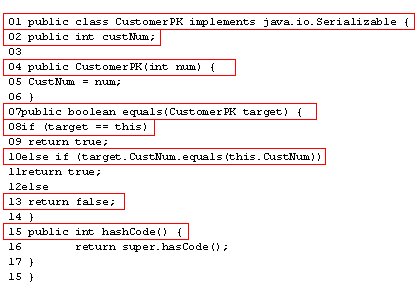
| line 01 | The primary key class is serializable. It can have any name. It helps to use the format of <name>PK.class as this fits in with <name>Home, etc. |
| line 02 | This primary key is for a customer number that is represented by a single int. |
| line 04 | The constructor is used to initialize the instance variables, custNum in this case. |
| line 07 | It is very important that the primary key contains an equal() method that can be used to compare two primary keys for equality. |
| line 08 | In this case we compare to see if they are the same object. |
| line 10 | If they are not the same object, then we compare them for equality. Primary keys that have the same value refer to the same persistent object by definition. |
| line 13 | If neither of the above are true we return false to indicate inequality. |
| line 15 | A primary key must implement the hashCode() method. |