| Lesson 4 | Data streams |
| Objective | Data streams use Java-defined data types |
Data Input Streams
DataInputStreams and DataOutputStreams have additional methods for reading data types. That is, instead of reading and writing bytes, they can read and write the data types defined by Java. For example, these classes have methods for reading and writing integers, floating-point numbers, characters, and boolean values.
Instances of both
DataInputStream and DataOutputStream are created based on an underlying stream. The idea is that these streams are piped. An instance of DataInputStream, for example, is tied to an instance of class InputStream.
The InputStream subclass reads the individual bytes; DataInputStream assembles them into Java's data types.
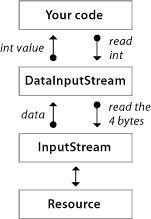
Explanation of Class Interactions
-
Your Code
- Your application code calls the
readInt()method on the DataInputStream instance. - This expects to read an integer value from the stream.
- Your application code calls the
-
DataInputStream
- The
DataInputStreamclass is a wrapper over InputStream. - It reads 4 bytes from the underlying
InputStreamand interprets them as anint.
- The
-
InputStream
- The
InputStreamclass is the lower-level stream providing the actual data. DataInputStreamreads from this raw byte stream.
- The
-
Resource
- The
InputStreamultimately gets data from a resource (e.g., a file, network socket, or other byte-based source). - The bytes travel up through
InputStreamtoDataInputStreamand finally get converted into anintin your code.
- The
- Your Code â Calls
readInt()onDataInputStream. - DataInputStream â Requests 4 bytes from
InputStream. - InputStream â Reads the raw bytes from a Resource.
- DataInputStream â Converts those 4 bytes into an
int. - Your Code â Receives the final integer value.
DataInputStream
When you create a
Here is a DataInputStream example.
It's also useful to know about two subclasses of InputStream and OutputStream that are associated with files. These are called FileInputStream and FileOutputStream. FileInputStream and FileOutputStream instances are created by specifying a file to associate with these streams. Once you create a FileInputStream instance, reading from this instance reads from the file. And of course, writing to an instance of class FileOutputStream writes to the file.
Example of DataInputStream
To create a
Then, you can use the
This way you will have read the entire line entered by the user--all in one shot. (Remember, to wrap the
You will see another example of
DataInputStream, you tie it to some other subclass of class InputStream. Here is a DataInputStream example.
It's also useful to know about two subclasses of InputStream and OutputStream that are associated with files. These are called FileInputStream and FileOutputStream. FileInputStream and FileOutputStream instances are created by specifying a file to associate with these streams. Once you create a FileInputStream instance, reading from this instance reads from the file. And of course, writing to an instance of class FileOutputStream writes to the file.
Example of DataInputStream
To create a
DataInputStream instance tied to the standard input, you can write:
DataInputStream stream = new DataInputStream(System.in);
Then, you can use the
DataInputStream methods, such as readInt(), which reads 4 bytes and assembles them into an int value. In Java 1.1, reading character-based data is handled by subclasses of Reader class.
To read text a line at a time, the recommended method is the readLine() method of BufferedReader class.
The bridge between InputStream and BufferedReader is InputStreamReader:
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(System.in); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr); String s = br.readLine();
This way you will have read the entire line entered by the user--all in one shot. (Remember, to wrap the
readLine() call in a try/catch block in case it throws an IOException.) You will see another example of
BufferedReader when we discuss the net package, coming up in the next module.
Program that uses FileInputStream and InputStreamReader to read in a File
The following program will read in the text file and at location c:\\input.txt and write it out to the console.
- Declare an object of type FileInputStream "inputStream" that contains the location of the input file.
- Chain that object with InputStreamReader
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.Reader;
public class InputStreamReaderDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("c:\\input.txt");
Reader reader = new InputStreamReader(inputStream);
int data = 0;
try {
data = reader.read();
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
while (data != -1) {
char charInput = (char) data;
try {
data = reader.read();
System.out.print(charInput); // this prints numbers
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
reader.close();
}
}
Read Using Buffered Reader - Exercise
Here is the second part of the exercise concerning reading from the standard input.
This exercise asks you to modify the program you wrote in the previous exercise to read from
Read Using Buffered Reader - Exercise
This exercise asks you to modify the program you wrote in the previous exercise to read from
DataInputStream.
Read Using Buffered Reader - Exercise
Java DataStreams - Quiz
When you finish, there is a quiz to review the material presented.
Java DataStreams - Quiz
Java DataStreams - Quiz